Artificial Intelligence / Machine Learning for Information Security
This course provides a broad introduction to the deployment of AI/ML for information security and related cybersecurity challenges.

We are professionals in the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) specializing in the information security domain. We provide:

This course provides a broad introduction to the deployment of AI/ML for information security and related cybersecurity challenges.
This program seeks to provide a practical overview on the process of designing, developing and implementing ethical AI programs as well as AI and data governance frameworks for organizations.
Overview
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are increasingly being deployed in information security either as a tool for defence, or as a weapon in cyberattacks. AI/ML are powerful tools in helping organisations minimise the impacts of cybersecurity threats. At the same time, it is imperative that AI/ML systems, including the models and algorithms, be protected against cyber-attacks. This course provides a broad introduction to the deployment of AI/ML for information security and related cybersecurity challenges. It explores various machine learning and data mining solutions to cybersecurity threats and problems. The course will review the vulnerabilities of AI/ML systems, risk mitigation solutions, using AI in cybersecurity defence and defending against AI-aided cyberattacks. This course will introduce participants to open source Machine Learning tools such as Jupyter notebook using packages like scikit-learn. Participants will learn the different algorithms in some of most widely adopted machine learning methods such as supervised learning, unsupervised learning and reinforcement learning.
TARGET AUDIENCE
COURSE OBJECTIVES
This course seeks to equip participants with:
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Upon completion of this course, the learner will be able to work in partnership with an AI specialist (if the learner is not already one), to:
Course Duration
2 days at 8 hours per day (total 16 hours)
Pre-requisites
COURSE OUTLINE
Topic 1: Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning for Information Security
Topic 2: Basics of Machine Learning and AI
Topic 3: Intrusion Detection System
Topic 4: Application of Machine Learning for Cybersecurity
Topic 5: Machine Learning in Cybersecurity Exercises
Topic 6: Case Studies
Delivery of Training
1 ML algorithms can be trained to identify patterns of normal network and system behavior, and then flag any deviation from that behavior as potentially suspicious.
2 ML algorithms can be used to analyze network traffic and identify patterns that are indicative of a cyber attack, such as a brute force login attack.
3 ML algorithms can be used to analyze files and identify patterns that are indicative of malware, such as known malware signatures or suspicious code patterns
4 ML algorithms can be used to identify patterns in emails and other communications that are indicative of phishing attempts.
5 SVM or Support Vector Machine is a supervised learning algorithm that can be used for classification and regression tasks. The algorithm finds the best boundary or "hyperplane" that separates the data into different classes. Once the boundary is determined, new data can be easily classified by seeing on which side of the boundary it falls. SVM can be used for both linear and non-linear data.
6 CNN or Convolutional Neural Network is a type of neural network architecture that is particularly well suited to image and video data. CNNs are designed to automatically and adaptively learn spatial hierarchies of features from input data. It does this by applying convolutional filters to the input data, which scan the data for specific patterns or features. CNNs are used in image classification, object detection, and video analysis.
7 LSTM or Long Short-term Memory is a type of Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) architecture. RNNs are neural networks that process sequential data, such as time series data or natural language. LSTMs are particularly useful for processing sequential data because they are able to maintain a "memory" of past information and selectively choose which information to use when making predictions. LSTMs are used in natural language processing, speech recognition, and time series forecasting.
8 Kali Linux is a Debian-based distribution that is primarily used for penetration testing, digital forensics, and security auditing. It comes with a wide array of tools for information gathering, vulnerability scanning, and exploitation. In the context of deploying AI/ML for cybersecurity, Kali Linux can be used to perform reconnaissance, vulnerability scanning, and exploit testing on target systems to generate data for training and testing of the AI/ML models.
9 Pandas is a Python library for data manipulation and analysis. It provides data structures and data analysis tools for handling and manipulating numerical tables and time series data. In the context of deploying AI/ML for cybersecurity, pandas can be used to clean, manipulate and prepare the data for training and testing of the ML models.
10 Keras is an open-source neural network library written in Python. It is a high-level API that allows for easy and fast prototyping of deep learning models. It can run on top of TensorFlow, Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit, or Theano. In the context of deploying AI/ML for cybersecurity, Keras can be used to quickly and easily build and test different deep learning models for tasks such as intrusion detection, malware detection, and phishing detection.
11 TensorFlow is an open-source software library for machine learning. It provides a set of tools for building, training, and deploying machine learning models, including deep neural networks. In the context of AI/ML deployment for cybersecurity, TensorFlow can be used to develop and train machine learning models that can detect and respond to cyber threats, such as malware, phishing attacks, and network intrusions. These models can be integrated into cybersecurity systems to provide real-time threat detection and response capabilities. Additionally, TensorFlow can also be used to analyze large amounts of network and endpoint data to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate a security incident.
Design, Develop and Implement Ethical AI Programs and AI and Data Governance Frameworks
Overview
In recent years, the world has seen significant advances in the sophistication and pervasive use of AI. Governments, enterprises and organizations have begun issuing principles, frameworks and recommendations on AI ethics and governance. The rise of a data and AI-driven economy necessitate enterprises, organizations and governments to build new capabilities on data and AI governance among its employees, partners, vendors and any entities that have any dealing in the deployment of AI. This program seeks to provide a practical overview on the process of designing, developing and implementing ethical AI programs as well as AI and data governance frameworks for organizations. It provides real world examples of how AI and data governance frameworks can be developed in practice.
Who should attend
Learning Outcomes
At the end of this 1-day16 program, participants will be able to:
Course Outline17
This course is divided into 2 parts:
PART 1: AI ETHICS AND GOVERNANCE
AI Ethics and Governance Framework
AI Ethical Principles
AI Governance Framework
Internal Governance Structure and Measures
Level of Human Involvement in AI-augmented Decision Making
Operations Management
Stakeholder Interaction and Communication
Model AI Governance Framework
The need to be:
Use Cases and Case Studies in Industry
PART 2: DATA GOVERNANCE
What is Data Governance
Elements of Data Governance Framework
Data Life Cycle Management
Operationalizing Data Governance
Legal and Compliance: Data Protection & Compliance Requirements
Monitoring of Data Governance Programs
Building a Culture of Data Privacy & Security
Data Governance in Practice
12 Chief Data Officers
13 Chief Marketing Officers
14 Chief Legal Officers
15 Chief Compliance Officers
16 This 1-day course can also be conducted over 2 days where the second day will focus on case studies and practical exercises to apply what has been learnt on Day 1. A typical program is 8 hours per day.
17 Credit is given to IMDA’s Model Framework for AI Governance (Second Edition) which has been released publicly for adoption by both industry and government. See further: http://go.gov.sg/ai-gov-mf-2



Training Strategy and Pedagogy
All training should result in organizations performing better. In delivering our courses, we adopt a learning and development framework called PEbAAL which stands for Performance-based, Experiential, Adaptive & Agile Learning.
Performance-based, Experiential, Adaptive & Agile Learning
The PEbAAL framework focuses on driving performance for organizations through experiential, adaptive and agile learning.
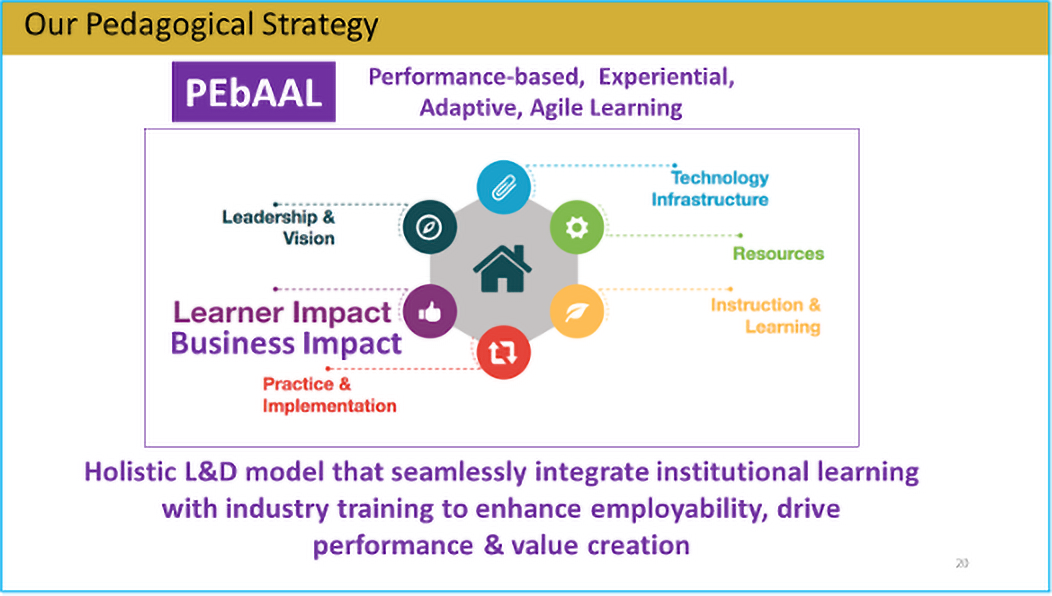

Our courses are focused on delivering outcomes and are tailored to suit the needs of organizations especially in the area of problem solving or value creation for organizations.
While most of the courses covered in this program are 1-day courses, the programs can be adapted to suit any duration to suit the needs of the organizations based on the principles of learning agility and flexibility.
Typically, C-suite executives attend very short courses lasting 2 to 3 hours only while middle management as well as the operational teams attend courses with a duration of between 1 to 2 days (8 hours per day).
Mode of Delivery
Our courses are typically tailored to suit the needs of the organizations especially the preferred mode of delivery. We typically adopt a hybrid model of learning including instructor-led synchronous as well as asynchronous training.
We also provide a cloud Learning Management System (LMS) system for organizations that requires such cloud systems to manage their learners’ learning journey. Where organizations have their own LMS, we offer services to integrate our contents and pedagogical strategies with their cloud LMS.
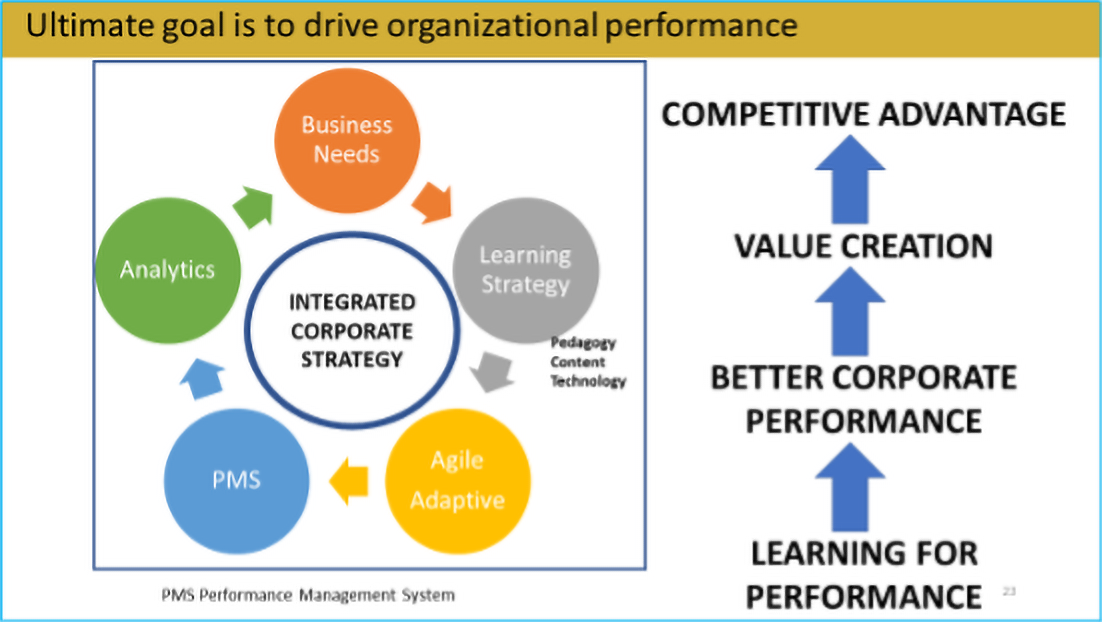
Business and Training Needs Analysis
The implementation of our PEbAAL framework typically starts with a business needs as well as a training needs analysis (TNA) involving both the organization as well as the learners, especially those at supervisory levels.
Upon completion of the TNA, we then embark on the learning program design and development before rolling out the program.
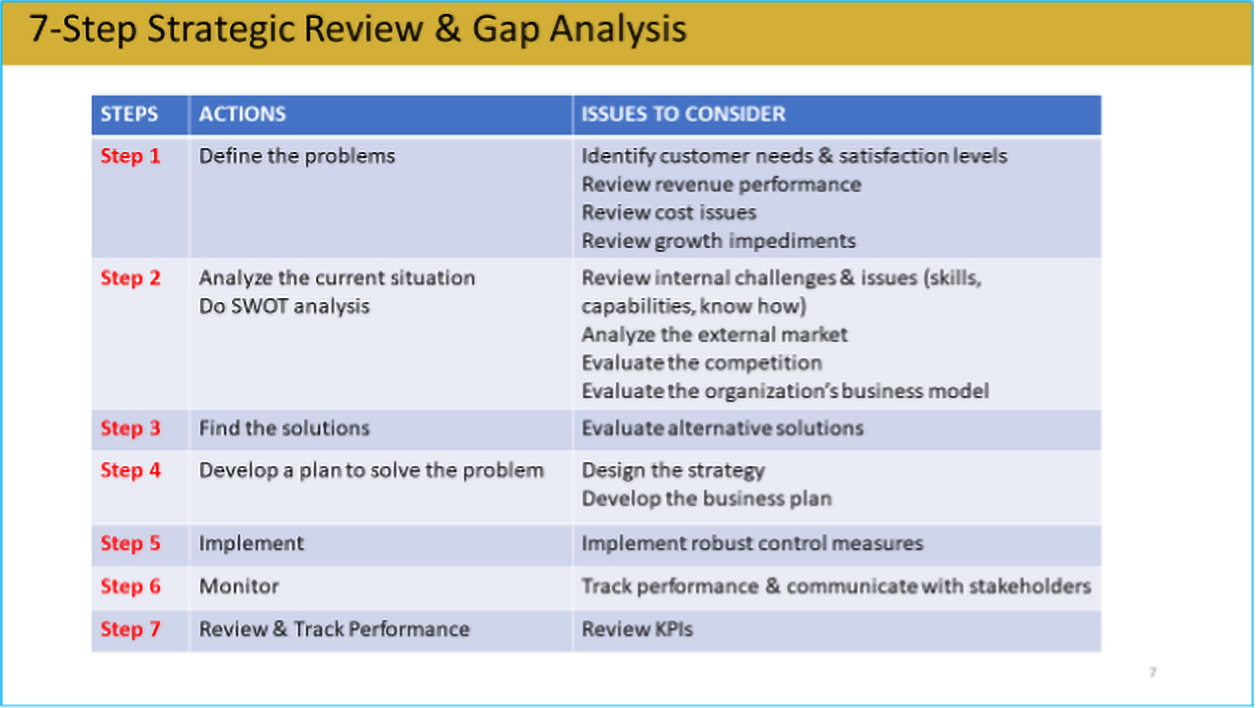
We adopt a 7-Step approach in carrying out a strategic review as well gap analysis for organizations before the commencement of any training programs.
Outcome-based Learning
We collaborate with our partners and clients to offer outcome-based learning that focuses on performance based on the key performance indicators for organizations.
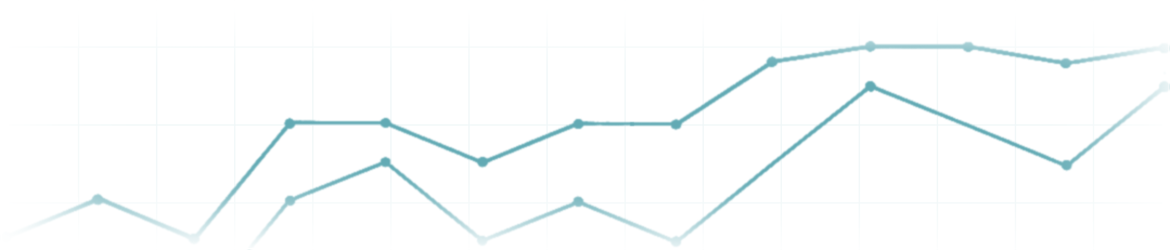
For evaluation of training effectiveness, we focus primarily on organizational or business impact as well securing the returns on investment in training and development as shown in the chart below:
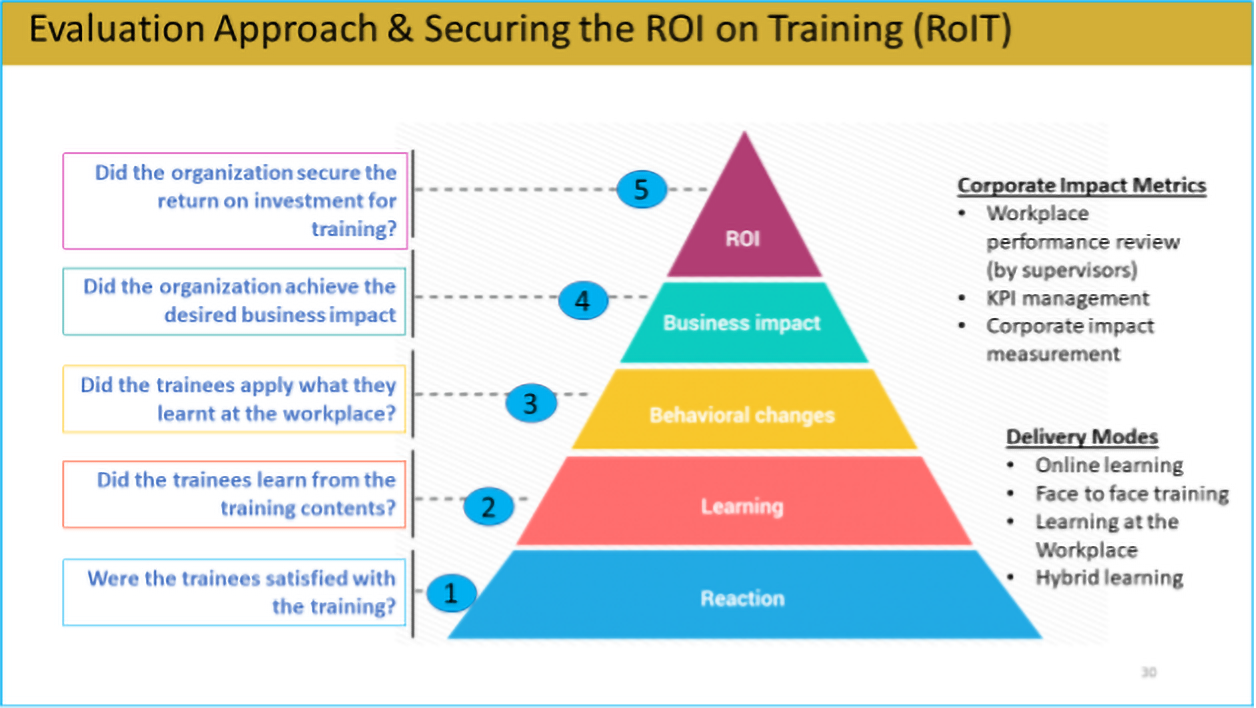
Implementation of Learning Outcomes at the Workplace
Under the PEbAAL framework, learning must ultimately lead to better organizational performance. Learnings must therefore be implemented at the workplace in order to secure the required organizational impact.
In our programs, we typically monitor how the learnings are implemented over a period of time (which varies according to the needs of the organization) as shown in the following chart:
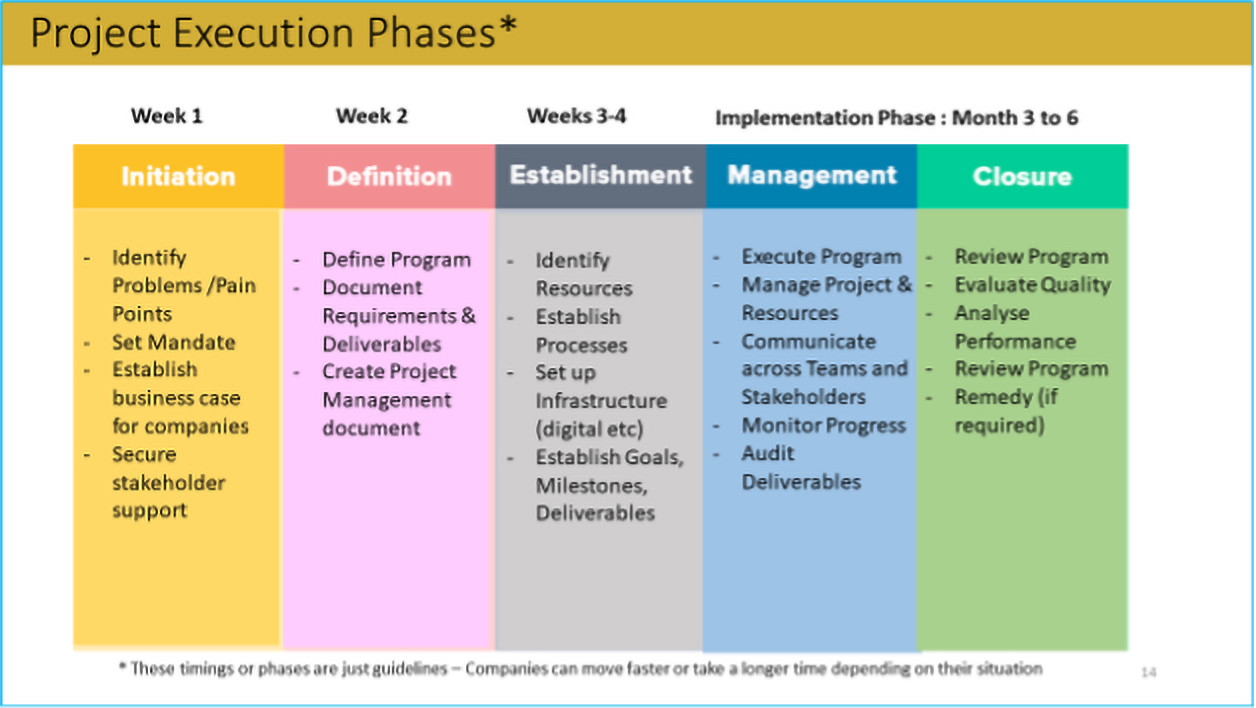


Zaid is an AI/data strategist & practitioner specializing in AI in finance & law, AI & data governance & AI in information security. An AI patent holder, his current practice revolves around driving value creation & higher performance through AI-enabled growth strategies. Zaid is currently an Executive Education Fellow at the National University of Singapore (NUS) School of Computing’s Advanced Computing for Executives centre where he runs programmes on AI Innovation Management, Intellectual Property Rights in AI Innovation & Commercialisation of AI Innovation. He has taught legal AI at the Singapore Management University School of Law. Zaid is deeply involved in AI R&D & innovation. His AI patent relating to risk management in a supply chain context was granted by the Intellectual Property Office of Singapore in December 2023. Author of 9 books spanning law, technology, intellectual property & AI, Zaid has over 35 years of professional experience. He has previously served as (i) Microsoft's Director for intellectual property & commercial software; (ii) Senior Legal Advisor to Singtel’s joint venture with Warner Bros & Sony Pictures; (iii) Chief Regulatory Legal & Compliance Officer at publicly-listed Telekom Malaysia; (iv) Associate, Khattar Wong & Partners (Singapore law firm) & (v) Singapore Government service. Zaid has a law degree from the National University of Singapore & completed his Masters in International Relations at the Fletcher School of Law & Diplomacy, Tufts University on a Fulbright scholarship. Zaid’s current professional practice work involves corporate growth strategy & performance management, intellectual asset management & strategic risk management including cybersecurity risk management.

Garrett is a data scientist and AI strategist with over 18 years of professional experience in leading data and AI projects, from strategy to design, future roadmap design, and delivery rollouts. He has held senior data science appointments with leading global consulting firms (including Accenture as Director of Applied Intelligence, ASEAN). He is currently Senior Director at Capgemini as Head of Data and Analytics for Southeast Asia. Garrett builds data practice and capabilities across the APAC region and has led data innovation programs in various sectors from financial services, consumer retail, telecommunications, healthcare, manufacturing to the public service sectors. Garrett is a Kaggle Masters data scientist with a vision that the art of data science will be the new art of strategy in this digital future. His key mission is to empower leaders to navigate uncertainties and make smarter decisions with human ingenuity, data, and artificial intelligence. He was a biostatistician for a Singapore research centre (Genome Institute of Singapore, part of ASTAR), performing statistical analysis and developing analytical models to decipher and break the genetic code for biomedical breakthroughs and advances. Garrett has co-authored several biomedical research papers and published on top medical journals and volunteered as data science and analytics instructor for schools and universities. Garrett graduated from Nanyang Technological University (2007) with a Master of Science (Bioinformatics) and Monash University (2004) with a Bachelor of Computing (Information and Business Systems).



To contact us regarding our resources and course offerings, email
Zaid Hamzah (Mr), our Founder and lead trainer at [email protected].